Deepseek V3 Released in late 2024 by the Chinese AI company DeepSeek, this model represents one of the largest and most advanced open-source AI systems available.
It boasts 671 billion parameters in a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture (with 37B parameters active per token) – an unprecedented scale designed to deliver state-of-the-art performance.
Trained on 14.8 trillion high-quality tokens and refined with advanced techniques, DeepSeek V3 achieves results comparable to proprietary models like GPT-4 across many benchmarks.
Importantly, DeepSeek V3 is fully open-source, with its code and model weights available under an MIT license.
This open approach means developers, researchers, and AI enthusiasts can freely use, modify, and integrate the model – a stark contrast to closed models that guard their code and require paid access.
In this article, we’ll explore DeepSeek V3’s key features, performance, how it stacks up against GPT-4 and Claude, and why it’s poised to be a game-changer in the AI landscape.
Key Features and Capabilities of DeepSeek V3
DeepSeek V3 packs a range of impressive features that set it apart in the AI ecosystem:
- Massive Scale & Innovative Architecture: With 671B parameters utilizing a Mixture-of-Experts design, DeepSeek V3 can allocate 37B parameters for each token it processes. This design enables the model to achieve high accuracy by leveraging specialized “experts” sub-models, all while keeping inference efficient through selective activation of parameters.
- Extensive Training Corpus: The model has been pre-trained on 14.8 trillion tokens of diverse, high-quality data. This enormous training set gives DeepSeek V3 a broad base of knowledge in domains ranging from natural language and code to mathematics and beyond. After pre-training, it underwent supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning phases to further hone its abilities (particularly for reasoning), resulting in a robust and well-rounded AI.
- Long Context Window (128K): One standout feature is its 128,000 token context window. This context size is orders of magnitude larger than most models. In practical terms, DeepSeek V3 can ingest and reason about extremely large documents or lengthy conversations without losing track of context. For example, it can analyze hundreds of pages of text in one go, making it ideal for tasks like processing technical manuals, entire books, or lengthy multi-turn dialogues.
- High Performance & Speed: DeepSeek V3 delivers results at both high quality and high speed. It generates text at up to ~60 tokens per second – about 3× faster than its predecessor (DeepSeek V2) – enabling more responsive interactions. Despite its size, it maintains efficient inference due to optimizations in its architecture and training (including multi-token prediction and FP8 precision techniques). In deployment, it’s engineered to utilize GPU hardware effectively, so users can get fast responses even for complex queries.
- Enhanced Reasoning & Coding Skills: A major focus for DeepSeek V3 is advanced reasoning capability. The model leverages techniques from DeepSeek’s R1 reasoning model to excel at complex problem solving. It has demonstrated superior performance in domains like mathematics, logic puzzles, and code generation. According to benchmark evaluations, DeepSeek V3 outperforms other open-source models and even matches or exceeds leading closed-source models in these areas. For instance, its coding abilities (e.g. writing and debugging code) have proven better than Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 and even OpenAI’s GPT-4 on certain programming challenges. It also shows strong multilingual proficiency, scoring highly on Chinese language tasks and other non-English benchmarks. This broad skill set makes DeepSeek V3 versatile – capable of handling tasks from answering general knowledge queries to writing complex software programs.
These features collectively make DeepSeek V3 one of the most formidable AI models available, especially outside the closed ecosystems of companies like OpenAI or Anthropic.
Next, we’ll dive deeper into how it actually performs and stacks up against those well-known models in real tests.
Performance and Benchmark Results
How does DeepSeek V3 perform in practice? The answer: extremely well.
Comprehensive evaluations and head-to-head benchmarks reveal that DeepSeek V3 is not just large on paper – it translates its size into concrete performance gains.
According to the DeepSeek team’s technical report, DeepSeek V3 consistently outperforms other open-source LLMs and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models like GPT-4 across a range of benchmarks.
In some cases, it even takes the lead over the proprietary giants:
- Reasoning and Math: An update in early 2025 (DeepSeek-V3-0324) further boosted the model’s reasoning skills by incorporating reinforcement learning techniques from the R1 model. As a result, DeepSeek V3 achieved scores exceeding those of a hypothetical “GPT-4.5” on challenging math and coding benchmarks. For example, on a graduate-level math competition (AIME 2024), DeepSeek V3 scored 39.2%, far ahead of Claude 3.5’s score of just 16%. This indicates a remarkable advantage in complex quantitative problem solving.
- Code Generation: Coding tasks are a strong suit for DeepSeek V3. In the popular HumanEval coding test (which measures a model’s ability to write correct Python functions), DeepSeek V3 achieved 82.6% pass@1, surpassing Claude 3.5’s 81.7% and GPT-4’s ~80.5% on the same test. It also excelled in a LiveCode benchmark (involving chain-of-thought reasoning for coding), again outscoring both Claude and GPT-4. These results show that developers can rely on DeepSeek V3 for tasks like generating code, debugging, and technical problem solving with confidence that its quality is at least on par with the best closed models.
- NLP and Knowledge Tasks: On general language understanding tasks in English, DeepSeek V3 demonstrates top-tier performance. For instance, it scored 88.5% on the MMLU benchmark, slightly edging out GPT-4’s 86.4% on that test (MMLU measures knowledge across 57 subjects). In realistic question-answering (Simple QA), DeepSeek V3 is competitive, though GPT-4 retains an advantage on some knowledge-intensive queries. Meanwhile, in Chinese language tasks, DeepSeek V3 shows exceptional capability for a non-proprietary model – scoring 91.6% on CLUE WSC (Chinese understanding) and 64.1% on a Chinese QA benchmark, outperforming GPT-4 in those categories. This makes it appealing for applications in multilingual settings, including Chinese, where it has been specially optimized.
- Continual Improvements: It’s worth noting that DeepSeek V3’s performance is not static. The DeepSeek team actively updates and refines the model, as seen with the V3-0324 upgrade in March 2025 which brought comprehensive capability upgrades. That update improved reasoning, coding, and even niche skills like front-end web development output and Chinese writing quality. The open-source nature means the community can also contribute to further improvements over time. DeepSeek V3’s trajectory is one of rapid enhancement, closing any remaining gaps with its competitors.
Benchmark comparisons from DeepSeek’s technical report, illustrating DeepSeek V3’s performance versus other AI models on key tasks.
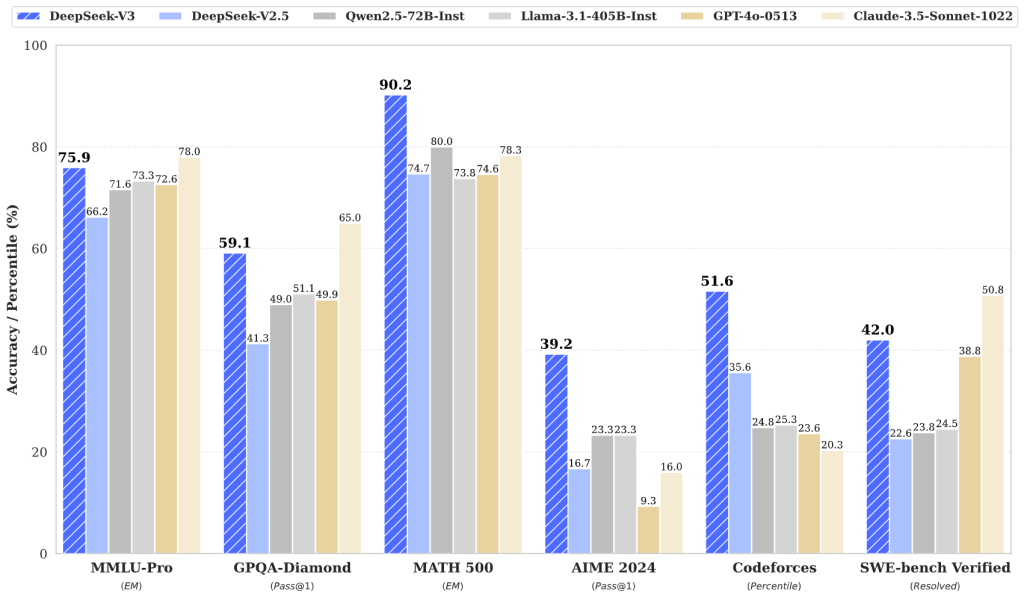
The chart shows DeepSeek-V3 (blue) and its updated version V3-0324 (hatched blue) achieving top scores in areas like math problem solving and coding.
Notably, DeepSeek V3 outperforms or matches models like Qwen (another open-source LLM) and even outpaces GPT-4.5 and Claude-Sonnet-3.7 on certain benchmarks.
For example, in the AIME math competition (fourth cluster of bars in the chart), DeepSeek-V3-0324 scores significantly higher than GPT-4.5. In coding evaluations (e.g. LiveCodeBench, last set of bars), DeepSeek V3 also leads the pack.
Higher bars indicate better performance, underscoring that DeepSeek V3 delivers competitive results at the cutting edge of AI.
Overall, the data makes one thing clear: DeepSeek V3 has firmly established itself among the top-performing LLMs in the world.
It matches or beats the “household name” models on many fronts, a stunning achievement for an open-source project developed in a fraction of the time and budget.
This naturally raises the question – how exactly does DeepSeek V3 compare to GPT-4 and Claude in practical terms? Let’s compare these models on several key dimensions.
DeepSeek V3 vs. GPT-4 vs. Claude: How Do They Compare?
To better understand DeepSeek V3’s impact, it’s useful to compare it directly with OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Anthropic’s Claude (Claude 2, the latest version as of mid-2025).
These are two of the most advanced proprietary AI models, and they represent the closed-source approach that DeepSeek aims to challenge.
Below is an overview of how the three models stack up in terms of specifications and features:
| Model | Size / Architecture | Context Window | Open Source? | Notable Strengths & Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek V3 | 671B parameters (Mixture-of-Experts); 37B active per token; Trained on 14.8T tokens | 128K tokens | Yes (MIT License) | – Excels in reasoning & coding tasks (outscoring GPT-4 in some benchmarks). – Fast generation (~60 tokens/s) and efficient training (only ~2.8M GPU hours). – Free to use and integrate; available via API or local deployment. |
| OpenAI GPT-4 | Estimated 1 trillion+ parameters (Transformer architecture; exact size undisclosed) | 8K tokens standard (up to 32K with extended version) | No (proprietary model) | – Multimodal: can accept image inputs as well as text. – State-of-the-art performance on many language tasks, highly versatile and creative – Backed by OpenAI’s ecosystem (plugins, widespread adoption), but usage is costly (≈$0.03/1K tokens). |
| Anthropic Claude 2 | Estimated ~70B+ parameters (Transformer; exact size not public) | 100K tokens | No (proprietary model) | – Focus on safe, conversational AI with helpful, less harmful responses – Extremely large context window (100K tokens) for reading long documents. – Strong in creative writing and summarization; available via API with free trials, but not open-source. |
Context Window: One of DeepSeek V3’s biggest advantages is context length. With a 128,000-token window, it far exceeds GPT-4’s context (8K standard, 32K max) and even slightly outstrips Claude’s 100K token context.
This means DeepSeek V3 can handle longer inputs than GPT-4 or Claude, which is crucial for tasks like analyzing lengthy documents or maintaining long conversations.
Claude 2 made headlines with its 100K context, but DeepSeek V3 has pushed this boundary even further, indicating a focus on enabling long-form and document-heavy applications.
Capabilities and Performance: In terms of raw intelligence and task performance, all three models are in the top tier, but there are nuanced differences.
GPT-4 is often considered the gold standard for overall performance and creativity, excelling in a wide range of tasks from writing to complex problem-solving.
Claude 2 is known for its friendly conversational style and strength in tasks requiring understanding of very long contexts (like summarizing large texts or analyzing long conversations) – Anthropic has emphasized safety and reliability, making Claude a good “assistant” model.
DeepSeek V3, meanwhile, has demonstrated equal or better performance in specific areas: for instance, its coding and mathematical reasoning abilities have matched or surpassed GPT-4 and Claude in benchmark tests.
DeepSeek’s team specifically targeted reasoning (with techniques like chain-of-thought distillation from their R1 model) to make V3 strong in logic-intensive tasks.
So while GPT-4 remains extremely strong across the board, DeepSeek V3 has closed much of the gap, particularly shining in technical domains (coding, math) and even multilingual tasks where many English-centric models struggle.
It’s also worth noting that GPT-4 currently has an edge in being multimodal – it can process images as input (and upcoming versions may handle audio/video).
DeepSeek V3 is text-only for now, though the developers have hinted that multimodal support is on the roadmap for the DeepSeek ecosystem.
Open-Source vs Closed: The most fundamental difference is openness.
DeepSeek V3 is completely open-source – its code and weights are freely available to the public – whereas GPT-4 and Claude are proprietary and closed.
This has several implications:
- Access and Cost: Anyone can use DeepSeek V3 without paying usage fees or being restricted by API limits. In fact, DeepSeek offers a free web demo and app for public use, and you can self-host the model if you have the hardware. By contrast, GPT-4 and Claude access is metered and can be expensive. To illustrate, GPT-4’s API pricing is around $30 per million input tokens and $60 per million output tokens. DeepSeek’s API (while currently offered free or low-cost during beta) is orders of magnitude cheaper – roughly $0.14 per million input tokens (yes, 14 cents) and $0.28 per million output tokens. That is over 200× cheaper than GPT-4’s rate. This drastic cost difference can make DeepSeek V3 extremely attractive for businesses and developers operating at scale. In fact, DeepSeek’s first models were developed with a tiny budget (~$5–6 million) compared to the tens or hundreds of millions spent on models like GPT-4, and those savings carry over to users in the form of low usage costs.
- Community and Innovation: With an open-source model, the AI community can inspect, contribute to, and build upon DeepSeek V3. This openness fosters collaboration and rapid innovation – researchers can fine-tune it for new languages or tasks, developers can optimize it for different hardware, and anyone can help find and fix weaknesses. We’ve seen with models like Meta’s LLaMA that open availability spurs a whole ecosystem of derivatives. DeepSeek V3 similarly invites community-driven advancements. Open models also bring transparency: their behavior can be audited more easily for biases or flaws since nothing is a black box. Closed models, while often very polished, do not allow this level of external scrutiny or customization.
- Use Cases and Flexibility: For certain users – especially enterprises and academics – open-source provides flexibility that closed models cannot. DeepSeek V3 can be deployed on-premises or in a private cloud, giving organizations full control over data and model usage. It also means the model can be integrated into products without legal hurdles, as long as one abides by the permissive MIT license. GPT-4 and Claude require sending data to third-party servers (which can be a deal-breaker for sensitive data scenarios) and one must adhere to those companies’ terms of service. DeepSeek’s open model, in contrast, can be used offline, fine-tuned on proprietary data, or modified to fit specific needs with no permission required.
Of course, there are also some considerations when comparing these models.
GPT-4’s closed nature means it benefits from continuous secret tuning and possibly additional proprietary data (like code or user feedback from millions of ChatGPT interactions) that an open model might not directly have.
Claude, being built by Anthropic with a focus on safety, might handle certain ethical or safety constraints more conservatively out-of-the-box, whereas open models like DeepSeek V3 can be fine-tuned by anyone (which is a double-edged sword: more flexibility, but also less built-in safeguarding).
It’s noted that DeepSeek, despite being open, does implement some content guidelines in its public demo (aligned with Chinese regulations, given the company’s origin).
However, those are not hard-coded into the model weights, so when self-hosted the behavior can be adjusted by the community or users as needed.
Bottom line: DeepSeek V3 holds its own against GPT-4 and Claude on technical merits, and it dramatically undercuts them on cost and openness.
Each model has its strengths – GPT-4 for broad reliability and multimodal abilities, Claude for safe long-form assistance, and DeepSeek V3 for open-source innovation and superb reasoning performance – but DeepSeek V3’s emergence signals that the gap between open and closed AI models is rapidly closing.
Open-Source Advantage and Community Impact
One of the greatest strengths of DeepSeek V3 is its open-source nature and the philosophy behind it.
The team’s mission emphasizes “open-source spirit + longtermism to inclusive AGI”, reflecting a commitment to share AI progress with the wider community. This approach has several key benefits:
- Democratizing AI Access: Because DeepSeek V3 is free to use, it allows anyone – from a solo developer or student to a startup or large enterprise – to leverage a top-tier language model without needing special access or a big budget】In an industry where the best AI systems are often locked behind APIs and paywalls, DeepSeek V3 stands out as an equalizer. For example, a researcher in academia can use DeepSeek V3 for NLP experiments or data analysis at minimal cost, rather than being limited to smaller open models or spending heavily on API calls to a closed model.
- Sparking Innovation and Research: Open-source models encourage experimentation. Developers can fine-tune DeepSeek V3 on niche domains (law, medicine, specific languages), integrate it into open-source libraries, or optimize it for performance (through techniques like quantization or distillation) – all of which accelerates innovation. Collaboration is key: improvements made by one group (say, an optimized training script or a new fine-tuned variant for coding) can be shared with all. This community-driven development can lead to features and optimizations that the original developers might not have thought of, making the model ecosystem richer. We’ve already seen enthusiasts reporting on DeepSeek V3’s capabilities and comparing notes on how it can be applied or improved, via blog posts and forums.
- Transparency and Trust: With the model weights and code available, users can audit DeepSeek V3’s inner workings】. This transparency helps build trust – for instance, one can check what data might have been in the training set, or verify that there are no hidden behaviors. In sensitive applications (healthcare, legal advice, etc.), some organizations prefer an open model they can inspect over a closed model that operates opaquely. Furthermore, researchers studying model biases or safety can probe DeepSeek V3 directly and publish their findings, contributing to safer and more reliable AI usage across the board.
- Rapid Iteration & Support: The open model has already seen rapid iteration. The DeepSeek community provides feedback, and the core team has issued updates (like V3-0324) addressing shortcomings and adding features. Users can expect that issues discovered in the model (errors in certain reasoning types, bugs in code output, etc.) might be quickly addressed either by official patches or community forks. In contrast, closed models update on the creators’ schedule and often without transparency into what changed. The open approach ensures continuous improvement in the open, for the benefit of all users.
It’s worth noting that DeepSeek’s open strategy is part of a broader trend in AI – following efforts like Meta’s LLaMA, EleutherAI’s models, and others that believe the future of AI should not be monopolized by a few large corporations.
DeepSeek V3’s success lends weight to the idea that open models can achieve parity with the best closed models.
This could lead to a more balanced AI landscape where users have a choice and innovation comes from many directions, not just big labs.
Of course, open-source AI also comes with responsibilities – ensuring ethical use, addressing misuse, and balancing openness with safety.
DeepSeek’s license is very permissive (MIT), allowing commercial and derivative use freely.
The company does include terms for their hosted services and has some usage guidelines to prevent misuse, but the onus is largely on the community and implementers to use the model responsibly.
So far, the reception has been positive, and we are seeing a healthy ecosystem forming around DeepSeek V3, including integrations into AI platforms (for example, services like FireworksAI offer on-demand deployment of DeepSeek V3 on dedicated GPUs).
Use Cases and Getting Started with DeepSeek V3
Thanks to its strong capabilities and open availability, DeepSeek V3 opens up a variety of use cases across different domains.
Here are a few scenarios and how you can get started:
- Coding Assistant: Given its prowess in code generation and debugging, DeepSeek V3 can serve as a powerful coding assistant. Developers can use the model to suggest code snippets, write functions, or even analyze and fix bugs in code. It has excelled at competitive programming problems and could be integrated into IDEs or developer tools. Getting started: DeepSeek provides an API platform that you can call from your applications. With simple REST or Python API calls, you can prompt the model with a coding question or a piece of code and get helpful outputs (similar to GitHub Copilot or ChatGPT’s Code Interpreter, but running on an open model). Fine-tuning on your project’s codebase is also possible to specialize the model’s knowledge.
- Data Analysis and Research: With its large context, DeepSeek V3 can ingest and analyze extensive textual data. Researchers can feed in large research papers, technical documentation, or datasets in text form and ask the model to summarize, extract insights, or answer questions about the content. This is useful for literature reviews or parsing long reports. The model’s strong reasoning ability means it can perform multi-step logical analysis, which is valuable in fields like law (analyzing case documents) or finance (parsing annual reports). Getting started: You can use the DeepSeek web demo to interactively chat with the model and provide it long text inputs (the web version supports up to 64K tokens currently). For full 128K context use, running the model locally or via the API is recommended, where you can adjust context length settings.
- Content Generation: DeepSeek V3 is capable of generating high-quality natural language, making it suitable for writing assistance, content creation, and creative tasks. Whether it’s drafting articles (like parts of this very piece!), writing marketing copy, or even composing poetry, the model’s expansive training corpus allows it to produce fluent and contextually relevant text. It has also been used in multilingual generation, so you can ask for outputs in languages other than English (its Chinese writing was specifically optimized in the latest update). Getting started: Use the DeepSeek Chat interface or API to prompt the model with a writing task. For example, you might say “Write a product description for a new smartphone” or “Translate the following English paragraph into Spanish.” The DeepSeek App (available for web and mobile) provides an easy chat-style interface for such interactions, with DeepSeek V3 running behind the scenes.
- Long-Form Conversations and Virtual Assistants: The combination of a long memory and fast response makes DeepSeek V3 well-suited for extended conversations, acting as a virtual assistant that “remembers” the whole dialogue. This could be employed in customer service bots that handle complex queries spanning many messages, or as a personal AI assistant that you can chat with over time without it forgetting earlier context. Getting started: Implementations of DeepSeek V3 in chatbot form can be done via the API (maintaining a conversation history up to 128K tokens). DeepSeek’s platform likely offers multi-turn conversation examples. There’s also an open-source chat web app by DeepSeek which you can try out for interactive conversations with the model.
Integration and Deployment: If you want to integrate DeepSeek V3 into your own software or pipeline, it’s very much possible. The model is available for download on platforms like GitHub and Hugging Face.
Keep in mind that running a 671B parameter model requires significant hardware – typically multiple high-memory GPUs or specialized inference engines.
DeepSeek V3 supports deployment via frameworks such as SGLang, LMDeploy, TensorRT-LLM, and others, and it can run in 8-bit (FP8) or 16-bit modes for efficiency.
If you don’t have the hardware to run it yourself, you can use cloud services or providers like Fireworks AI that host the model for you on-demand.
Accessing the model is straightforward: you can call the API endpoint (after obtaining an API key from DeepSeek’s platform) or load the model checkpoint in a library like Hugging Face Transformers if you have the resources.
The DeepSeek documentation and community provide guidelines and support for deployment and fine-tuning.
Before using DeepSeek V3 in a production setting, it’s wise to test it thoroughly for your specific use case, as with any AI model.
While it’s extraordinarily capable, each model has quirks, especially with certain prompt phrasing or in edge cases.
Because you have full control, you can also apply custom moderation or filtering on its outputs if needed (for instance, to ensure it adheres to your application’s safety requirements).
Conclusion: A New Era for Open AI Models
DeepSeek V3 signifies a pivotal moment in the AI industry. It proves that an open-source model, developed by a relatively young organization, can reach the upper echelons of performance – essentially matching models from AI giants that previously seemed untouchable.
For AI developers and businesses, this is an exciting development: it means you are no longer forced to choose between state-of-the-art capability and open access – DeepSeek V3 offers both.
The model’s combination of massive scale, strong results, and permissive availability is driving a wave of interest and adoption.
Looking ahead, the existence of DeepSeek V3 (and its future iterations) could intensify competition in the AI field, pushing even the well-funded proprietary model makers to accelerate their progress or adjust pricing.
Open models like this one can also serve as a foundation for more specialized systems; we might see variants or fine-tuned models built on DeepSeek V3 for domains like medicine or law, developed by the community.
This all contributes to a richer, more diverse AI ecosystem.
For users and organizations, the key takeaway is that cutting-edge AI is becoming more accessible than ever.
If you’ve been impressed by GPT-4 or Claude but hesitant about their restrictions or cost, DeepSeek V3 is absolutely worth a look.
It represents an open-source challenger that brings top-notch AI within reach of anyone curious enough to try it.
As the DeepSeek team aptly put it, this is “just the beginning” – we can look forward to multimodal capabilities, further improvements, and new innovations built on the DeepSeek platform in the near future.
The open-source AI revolution is gaining momentum with DeepSeek V3 at the forefront.
Whether you’re a developer seeking a powerful model to build your application, a researcher exploring the limits of AI, or an enthusiast wanting to experiment with the latest AI advances, DeepSeek V3 invites you to be part of this new era where AI excellence meets open accessibility.
The playing field in AI is leveling, and that’s good news for everyone.